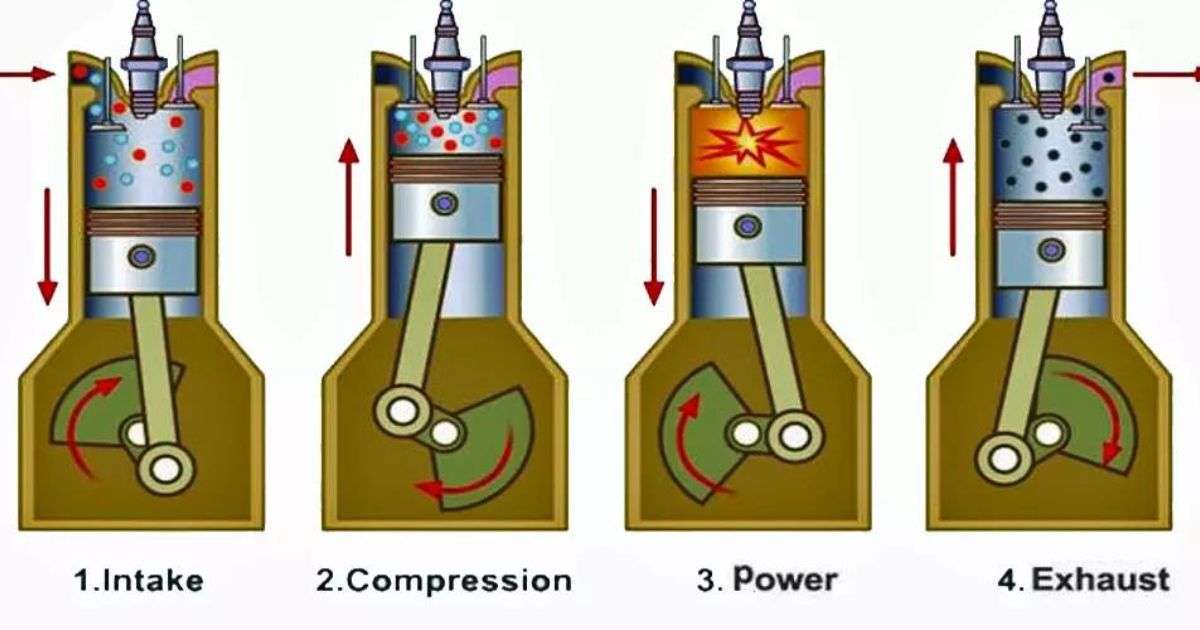
A 4-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine. Have you ever popped the hood of a car and stared in awe at the complex machinery within? If so, you’ve likely encountered the marvel of engineering known as the 4-cycle engine, also sometimes called a 4-stroke engine. This amazing invention is the heart of most modern gasoline-powered vehicles, from the car you drive every day to lawnmowers and even some airplanes. But how exactly does this marvel work? Let’s delve into the world of 4-cycle engines, breaking it down into easy-to-understand terms.
What is a 4-Cycle Engine?
In simple terms, a 4-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine. This means it burns fuel (usually gasoline or diesel) inside a sealed chamber to create energy. That energy, in turn, is used to power the vehicle or machine. But unlike some simpler engines, a 4-cycle engine accomplishes this feat in a very specific way: through four distinct strokes of the piston moving up and down within a cylinder.
The Four Strokes of a 4-Cycle Engine
Here’s where the magic happens! To understand what a 4-cycle engine is, we need to understand these four crucial strokes:
- Intake Stroke (Induction): Imagine taking a deep breath. That’s what happens in the first stroke. The piston moves down in the cylinder, creating a vacuum. This sucks in a mixture of air and fuel (usually gasoline) through an open intake valve. The exhaust valve remains closed during this process.
- Compression Stroke: Now, picture yourself holding your breath and squeezing your chest. That’s similar to the compression stroke. With both the intake and exhaust valves closed, the piston moves back up the cylinder, squeezing the air-fuel mixture into a much smaller space. This compression makes the mixture more volatile, ready for combustion.
- Power Stroke (Combustion): This is where the real action happens! At the top of the compression stroke, a spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture. The burning fuel rapidly expands, pushing the piston back down the cylinder with tremendous force. This force is what rotates the crankshaft, converting the power of combustion into mechanical energy.
- Exhaust Stroke: With the party over, it’s time to clean up. The exhaust valve opens as the piston moves back up the cylinder for the final time. This pushes out the burned gases, clearing the way for a fresh air-fuel mixture in the next intake stroke.
Also read: https://headlineocean.com/the-mahindra-xuv-3xo-engine-specifications/
Putting It All Together: The 4-Cycle Engine Cycle
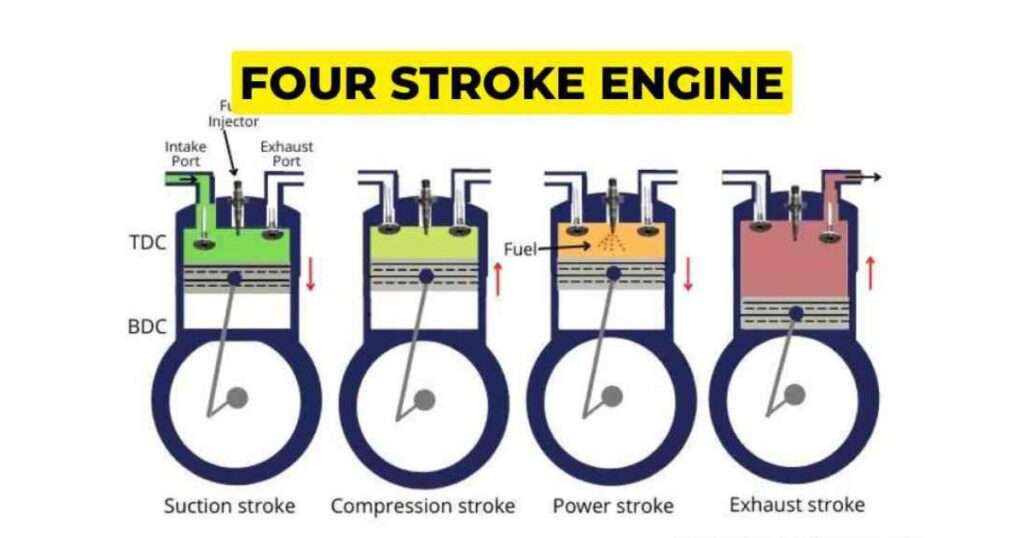
These four strokes happen in a continuous cycle. As the crankshaft rotates twice for each complete cycle of the piston, a 4-cycle engine gets its name. This constant cycle of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust is what keeps the engine running and generating power.
- Why You Should Care About 4-Cycle Engines
Understanding what a 4-cycle engine is can be surprisingly beneficial. Not only does it give you a newfound appreciation for the complex mechanics powering your car, but it can also help you troubleshoot minor engine issues or simply impress your friends with your newfound knowledge.
- 4-Cycle Engines vs. 2-Cycle Engines
It’s important to note that 4-cycle engines aren’t the only game in town. There are also 2-cycle engines, which are often found in smaller machines like lawnmowers and some motorcycles. These engines complete the same tasks (intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust) but do so in just two strokes. However, 4-cycle engines are generally considered more efficient and cleaner burning than their 2-cycle counterparts.
The Benefits of 4-Cycle Engine
So, what makes 4-cycle engines so popular? Here are some of their key advantages:
- Efficiency: The separate strokes allow for more efficient use of fuel, leading to better gas mileage.
- Cleaner Emissions: By completely separating the intake and exhaust processes, 4-cycle engines produce fewer harmful emissions compared to 2-cycle engines.
- Durability: The distinct strokes reduce friction and wear on the engine components, leading to a longer lifespan.
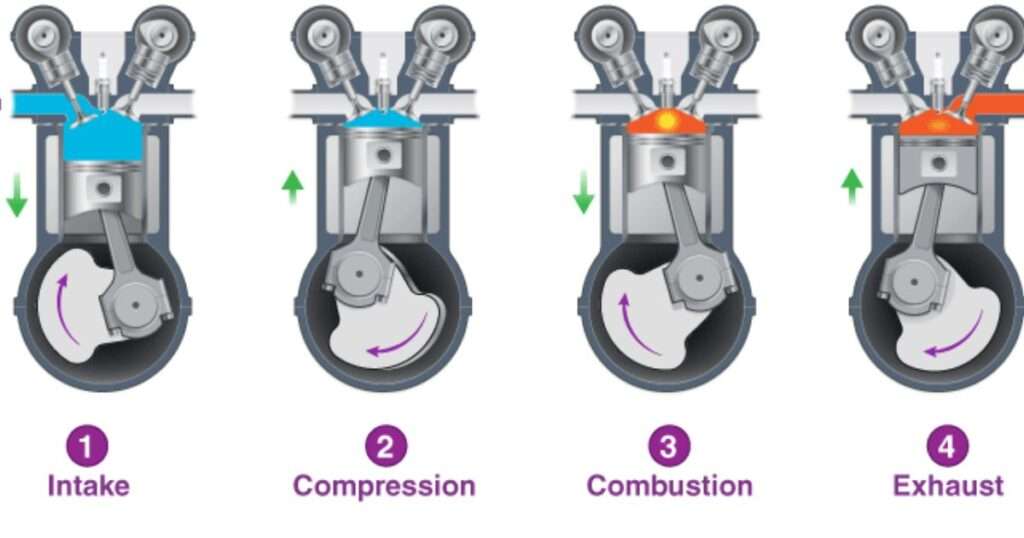
The Future of 4-Cycle Engines
Even though 4-cycle engines are a well-established technology, engineers are constantly looking for ways to improve them. One area of focus is on increasing fuel efficiency further, reducing emissions even more, and developing alternative fuels that can be used in these engines.
The trusty 4-cycle engine has served us well, but the future holds both challenges and opportunities. While electric vehicles gain traction, 4-cycle engines are far from obsolete. The focus is on making them cleaner and more efficient.
- Challenge: Emissions
Stricter regulations demand cleaner engines. Engineers are looking at improved combustion processes, advanced emission control systems, and even alternative fuels like biofuels and hydrogen to reduce a 4-cycle engine’s environmental impact.
- Opportunity: Efficiency
Every drop of fuel counts. Advancements in materials science, computer-controlled engine management, and even entirely new engine designs are being explored to squeeze more miles out of every gallon.
- Co-existing with Electric
4-cycle engines might not power every car in the future, but they’ll likely remain relevant. Hybrid vehicles that combine electric motors with 4-cycle engines offer a balance of efficiency and range. Additionally, for applications where long-distance travel or heavy loads are crucial, 4-cycle engines with improved efficiency might still be the preferred choice.
In conclusion, the 4-cycle engine’s future hinges on innovation. By addressing emissions and efficiency, it can remain a vital part of our transportation landscape, even as electric vehicles rise in popularity.
Congratulations! You’ve unlocked the secrets of the 4-cycle engine. This marvel of engineering, with its rhythmic dance of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, keeps our cars humming and our lawnmowers buzzing. This knowledge empowers you to appreciate the complex mechanics at work, troubleshoot basic engine issues, or simply impress your friends with newfound automotive expertise. Remember, 4-cycle engines are efficient, clean-burning workhorses, and with advancements in technology, they’ll likely continue to be a force on the road, even as we explore new transportation frontiers.
1. What is considered a 4-cycle engine?
Four Stroke Cycle Engines. A four-stroke cycle engine is an internal combustion engine that utilizes four distinct piston strokes (intake, compression, power, and exhaust) to complete one operating cycle.
2. What is the difference between 2-cycle and 4-cycle engines?
Both engines use the combustion cycle to produce energy. The main difference between a 2- and 4-stroke engine is that a 4-stroke engine goes through four stages, or two complete revolutions, to complete one power stroke. A 2-stroke engine goes through 2 stages, or one complete revolution, to complete one power stroke.
3. What is the four-cycle of an engine?
Four-stroke cycle used in gasoline/petrol engines: intake (1), compression (2), power (3), and exhaust (4). The right blue side is the intake port and the left brown side is the exhaust port.
4. Do 4-cycle engines need oil?
A 4-stroke engine needs to circulate oil throughout to lubricate these moving parts, whereas a 2-stroke engine only needs to lubricate the internal components of the combustion chamber, which is achieved by mixing the correct oil-to-fuel ratio.
5. How do I know if my engine is a 4-cycle?
A 2-cycle engine has one fill port with a cap that has fuel pump and oil can icon. The cap will usually state the oil to fuel mix ratio. A 4-cycle engine has two fill ports with each cap separately identifying the fuel tank from the oil sump.
6. Why is an engine called a 4-cycle engine?
This type of internal combustion engine is called a four-stroke engine because there are four movements, or strokes, of the piston before the entire engine firing sequence is repeated. The four strokes are described below with some still figures.
7. Which is faster, 2-stroke or 4?
While 2-stroke engines may offer quicker acceleration and higher power-to-weight ratios, 4-stroke engines excel in providing steady power and torque, along with being more environmentally friendly.
8. Is there a 6 stroke engine?
Subsequently, other six-stroke engine designs were explored, such as Dyer, Bajulaz, Velozeta, NIYKADO, Crower, and various two-piston designs (Gupta et al. 2018; Nimsiriwangso et al. 2019). These designs aimed to improve fuel consumption, increase power output, reduce pollution, and offer fuel versatility.
9. What is a disadvantage of a 2-cycle engine?
Two-stroke engines don’t last nearly as long as four-stroke engines. The lack of a dedicated lubrication system means that the parts of a two-stroke engine wear a lot faster. Two-stroke oil is expensive, and you need about 4 ounces of it per gallon of gas.
10. What are the disadvantages of a 4-stroke engine?
Less powerful :- As power gets delivered once every 2 rotations of crankshaft(4 strokes), hence 4 stroke is less powerful. Expensive :- A four stroke engine has much more parts than 2 stroke engine. So they often require repairs which leads to greater expense.